:::
News
The Secret Diet of the Mola Mola: They Don't Just Eat Jellyfish!
- PostDate:2025-03-10
A recent study by the Fisheries Research Institute has discovered that Mola Mola (Family Molidae) species do not exclusively feed on jellyfish. Their diet is more diverse than previously thought, including jellyfish, crustaceans, and benthic species. Additionally, different species within the family exhibit varying dietary resource allocation. This research is the first international study to examine the feeding habits of all species within the Molidae family, with the findings published in Environmental Biology of Fishes in 2024.
The Fisheries Research Institute notes that five species across three genera of Mola Mola exist worldwide, making them the largest existing species of bony fish. Often misidentified as manta rays, these fish are common in the eastern waters of Taiwan, where the Ocean Sunfish (Mola ramsayi) accounts for 80-90% of the Mola Mola catch. Mola Mola species are widely distributed globally in tropical and temperate seas, with habitats ranging from the ocean surface to 1,000 meters in depth. According to catch records, their population has declined annually due to high bycatch rates. As a result, the International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN) lists Mola Mola as vulnerable. Research on their diet has revealed that Mola Mola species primarily consume jellyfish but feed on other species in surface waters. The Ocean Sunfish (Mola ramsayi) primarily consumes salps and feeds on benthic organisms. In contrast, the Spotted Ocean Sunfish has been found to consume crustaceans and squid, with no jellyfish detected.
Through controlled studies on feeding habits and resource allocation, this research provides insight into the relationship between Mola Mola and their prey. Identifying areas with high food density can help determine high-risk habitats for Mola Mola, allowing recommendations for long-line fishing operations to avoid these regions and reduce bycatch risks. Further studies on the ecology and distribution of Mola Mola species will serve as a foundation for future fisheries resource management.

Photo 1. Literature Review on the Feeding Habits of Mola Mola Species: Number of Studies and Recorded Prey Types. Colors represent different species within the Mola Mola family.
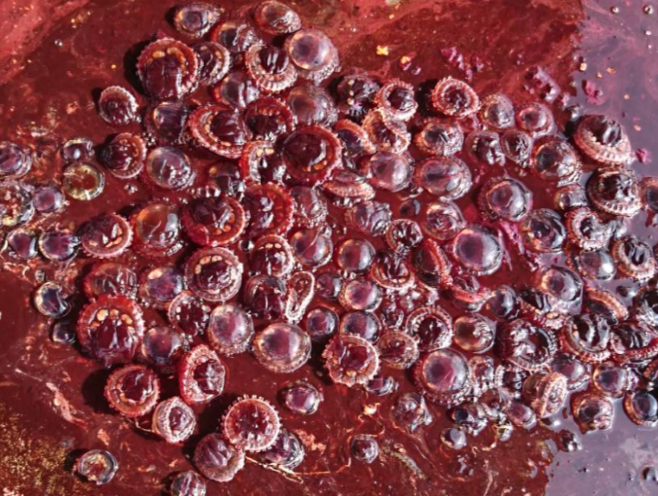

Photo 2. Stomach Contents of Mola Mola Species – Jellyfish
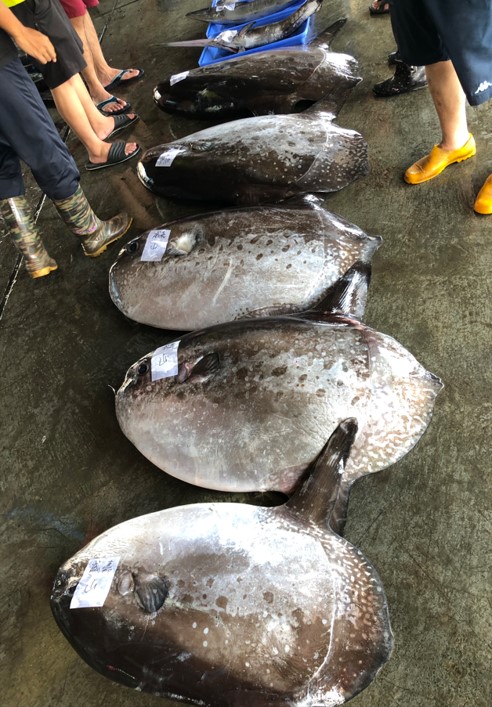

Photo 3. Mola ramsayi (Ocean Sunfish) captured in the eastern waters of Taiwan
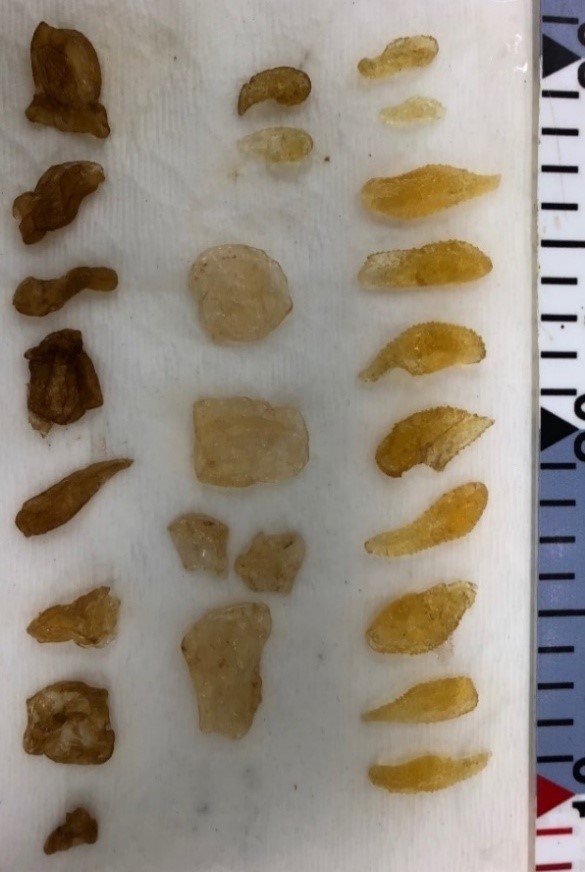
Photo 4. Stomach contents of Mola ramsayi – Salps and Scyphozoans
Contact Person:
Yuan-Shing Ho, Director, Eastern Fishery Research Center
Tel: (089) 850090 #301
Author:
Ching-Chun Chang, Assistant Researcher
Tel: (089) 850090#409
The Fisheries Research Institute notes that five species across three genera of Mola Mola exist worldwide, making them the largest existing species of bony fish. Often misidentified as manta rays, these fish are common in the eastern waters of Taiwan, where the Ocean Sunfish (Mola ramsayi) accounts for 80-90% of the Mola Mola catch. Mola Mola species are widely distributed globally in tropical and temperate seas, with habitats ranging from the ocean surface to 1,000 meters in depth. According to catch records, their population has declined annually due to high bycatch rates. As a result, the International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN) lists Mola Mola as vulnerable. Research on their diet has revealed that Mola Mola species primarily consume jellyfish but feed on other species in surface waters. The Ocean Sunfish (Mola ramsayi) primarily consumes salps and feeds on benthic organisms. In contrast, the Spotted Ocean Sunfish has been found to consume crustaceans and squid, with no jellyfish detected.
Through controlled studies on feeding habits and resource allocation, this research provides insight into the relationship between Mola Mola and their prey. Identifying areas with high food density can help determine high-risk habitats for Mola Mola, allowing recommendations for long-line fishing operations to avoid these regions and reduce bycatch risks. Further studies on the ecology and distribution of Mola Mola species will serve as a foundation for future fisheries resource management.

Photo 1. Literature Review on the Feeding Habits of Mola Mola Species: Number of Studies and Recorded Prey Types. Colors represent different species within the Mola Mola family.

Photo 2. Stomach Contents of Mola Mola Species – Jellyfish

Photo 3. Mola ramsayi (Ocean Sunfish) captured in the eastern waters of Taiwan

Photo 4. Stomach contents of Mola ramsayi – Salps and Scyphozoans
Contact Person:
Yuan-Shing Ho, Director, Eastern Fishery Research Center
Tel: (089) 850090 #301
Author:
Ching-Chun Chang, Assistant Researcher
Tel: (089) 850090#409
